Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamamura, Shuji*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Aramaki, Noritaka*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Kaneko, Katsuhiko*
Groundwater, 56(1), p.118 - 130, 2018/01
Groundwater saturated with gas forms bubble under atmospheric pressure, bothering most authorized methods to determine in-situ dissolved gas concentrations. To circumvent this problem, a simple theory to quantify effect of 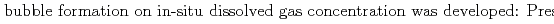 [bar]) of a gas component "
[bar]) of a gas component "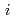 " (e.g., CH
" (e.g., CH , CO
, CO and H
and H ) in equilibrium with in-situ dissolved concentration (
) in equilibrium with in-situ dissolved concentration (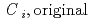 [mol L
[mol L  ]) was related to partial pressure of the
]) was related to partial pressure of the 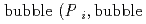 [bar]) emerged from groundwater in the form:
[bar]) emerged from groundwater in the form: 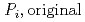 =
= 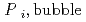 +
+ 
 (k
(k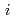 '
' 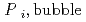 /(
/(
 k
k '
' 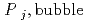 )), where
)), where 
 [bar] is groundwater pressure difference before and after the
[bar] is groundwater pressure difference before and after the 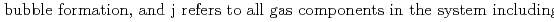 " The k
" The k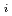 ' and k
' and k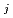 ' corresponds to the Henry's constant [bar L mol
' corresponds to the Henry's constant [bar L mol ] of
] of 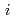 (k
(k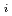 ) and
) and  (k
(k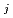 ), respectively, except for k
), respectively, except for k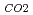 ', which is pH-dependent function. Dissolved CH
', which is pH-dependent function. Dissolved CH concentrations were successfully estimated by the model within the error of
concentrations were successfully estimated by the model within the error of  4.0% from the direct measurements by the sealed sampler method. Similar TIC concentration in the groundwater before and after the rm bubble formation was consistent with the model prediction. The wide application of the model is suggested without selecting sampling locations.
4.0% from the direct measurements by the sealed sampler method. Similar TIC concentration in the groundwater before and after the rm bubble formation was consistent with the model prediction. The wide application of the model is suggested without selecting sampling locations.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Mizuno, Takashi; Hirota, Akinari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Masaki; Ishii, Eiichi; Ono, Hirokazu; Kawate, Satoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Okumura, Fumiaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Murakami, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsushita, Kentaro; Ito, Kei*; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
no journal, ,
In a sodium-cooled fast reactor, from the viewpoint of prevention of core reactivity disturbance, it is important to evaluate the bubbles and dissolved gas behavior in the primary coolant system due to gas entrainment. For this reason, a numerical simulation code SYRENA for bubble and dissolved gas behavior analysis in the fast reactor primary coolant system has been developed in JAEA. In this study, a flow network model of SYRENA for tank type reactor was constructed and numerical simulations aiming to compare the bubble behavior characteristics in the loop type reactor and the tank type reactor was performed as a part of the fundamental validations of the flow network model of SYRENA. As the result, it was clarified that the differences regarding the bubbles and dissolved gas behavior between two different type reactors were indicated.